RESEARCH
Highly Efficient Energy Use and Resource Recycling
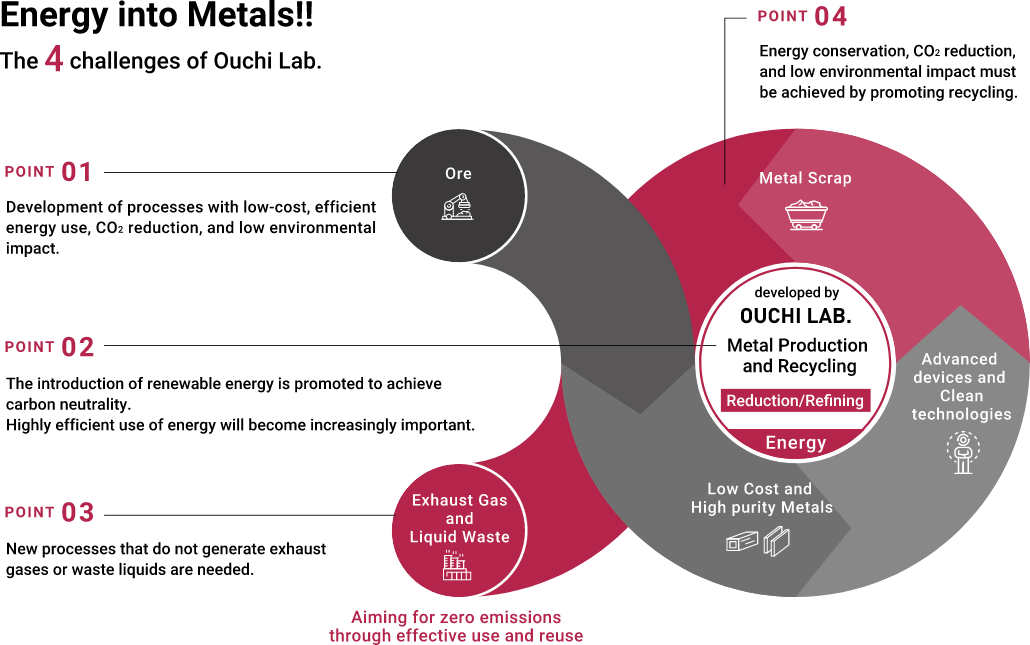
Ouchi Laboratory is engaged in the research and development of new smelting and recycling processes for nonferrous metals with an aim to achieve “Highly Efficient Use of Energy and Resource Recycling.” We contribute to the development of advanced technologies by efficiently converting energy into metal forms. We also contribute to the realization of a sustainable society by developing innovative recycling processes that actualize resource recycling.
KEY RESEARCH TOPICS
Precious metals(PMs)
The gold and platinum group metals are key materials for advanced de-vices.
We develop new processes to effi-ciently recover PMs from metal scraps using “Anodic deposition” though the anionic dissolution of PMs in molten salts and molten salt electrolysis.

Reactive metals
Lithium, sodium, calcium, magne-sium, aluminum, zinc, and rare earth metals are used in energy materials, functional materials, and structural materials and reducing agents for metal production.
We develop innovative smelting and refining processes by controlling electrochemical reactions in molten salts.

Titanium
Producing titanium metal from ore involves a specific multi-stage, en-ergy-intensive, and high CO2 emis-sion process.
To replace such a time-consuming and high-cost process, we develop new processes to efficiently remove oxygen from titanium scrap and ena-ble "upgrade recycling" by producing purer titanium compared to that pro-duced from the ore.

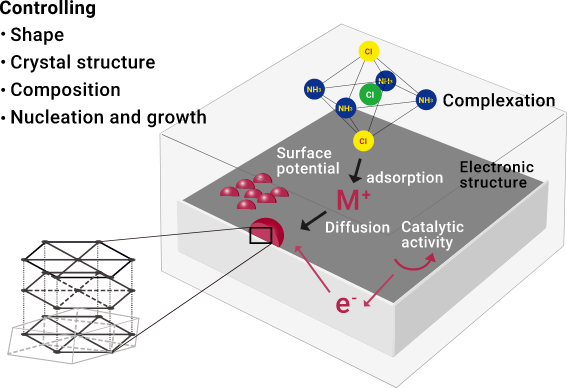
Electrochemical plating
For advanced devices, electrochemi-cal plating is indispensable for fabri-cating wires and contacts, corrosion protection materials, functional com-ponents, catalysts, etc.
We develop innovative plating tech-nologies to produce structures and films with the desired functions and shapes by controlling the behavior of metal ions, electrode surface poten-tial, and crystal structure.

Precious metals (PM)
The gold and platinum group metals are key materials for advanced de-vices.
We develop new processes to effi-ciently recover PMs from metal scraps using “Anodic deposition” though the anionic dissolution of PMs in molten salts and molten salt electrolysis.

Print circuit boards (PCBs)
Au is used in PCBs, the main components of electrical and electronic equipment

Automobile catalyst
The main application of Platinum (Pt), Palladium (Pd), Rhodium (Rh)

Reactive metals
Lithium, sodium, calcium, magne-sium, aluminum, zinc, and rare earth metals are used in energy materials, functional materials, and structural materials and reducing agents for metal production.
We develop innovative smelting and refining processes by controlling electrochemical reactions in molten salts.
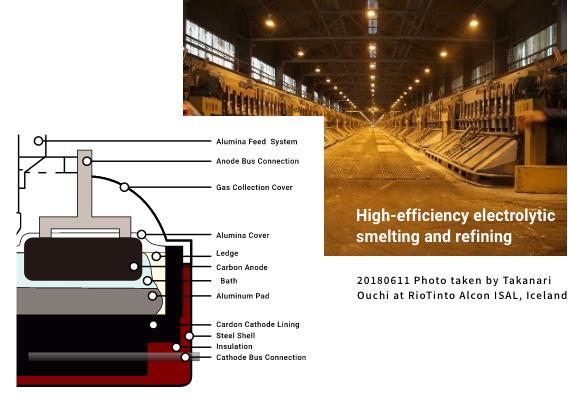
Titanium (Ti)
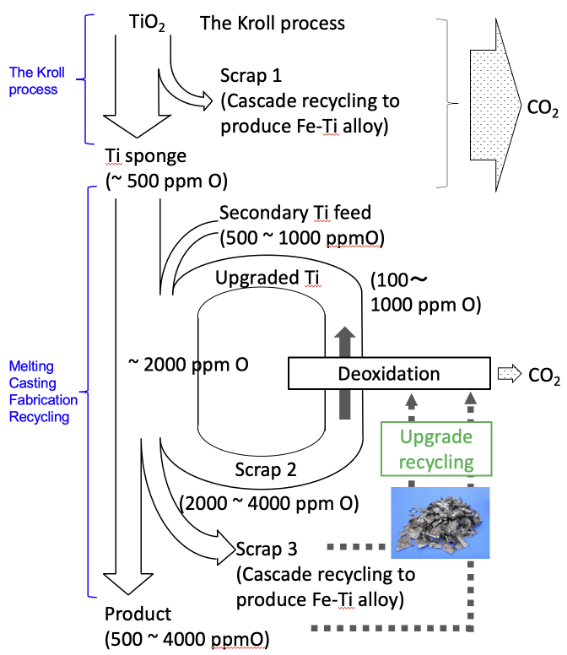
Producing titanium metal from ore involves a specific multi-stage, en-ergy-intensive, and high CO2 emis-sion process.
To replace such a time-consuming and high-cost process, we develop new processes to efficiently remove oxygen from titanium scrap and ena-ble "upgrade recycling" by producing purer titanium compared to that pro-duced from the ore.
The process of producing Ti metal from ore is a very specific multi-stage process with high energy consumption and high CO2 emissions. Long time consuming and high cost (USD10,000/ton) (cf. Al: USD2,000/ton).
We develop a new process to efficiently remove oxygen from Ti scrap and enable "upgrade recycling" by producing Ti purer than virgin Ti primarily produced from ore.
 Price reduction, energy saving CO2 reduction
Price reduction, energy saving CO2 reduction
Electrochemical plating
For advanced devices, electrochemi-cal plating is indispensable for fabri-cating wires and contacts, corrosion protection materials, functional com-ponents, catalysts, etc.
We develop innovative plating tech-nologies to produce structures and films with the desired functions and shapes by controlling the behavior of metal ions, electrode surface poten-tial, and crystal structure.